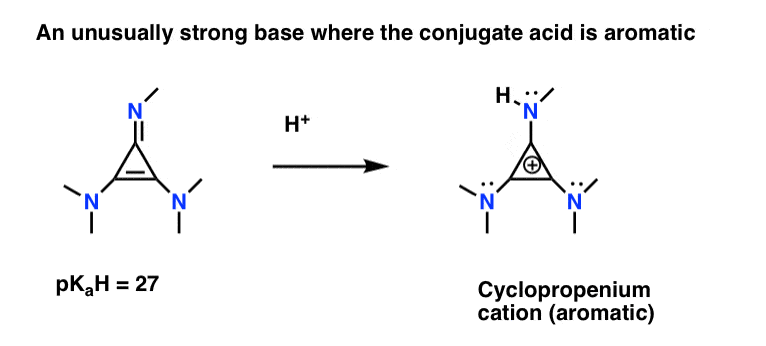
Answer (1 of 4) This is an interesting question We have to look at two factors herehydration energy and steric hinderance As we know by theory of the inductive effect the trialkyl version should be more basic simply because of the increasedThe order of basicity in ammonia is different in gaseous phases vs aqueous phases due to hydrogen bonding So in gaseous phases it's the well known 3' > 2' > 1'> NH3 Just so we're on the same page, this is due to the inductive effect of electron donating alkyl groupsthey destabilize the lone pair on nitrogen atom, making nitrogen more basic #1 I was going through the EK Chemistry lesson, and they explained that Guanidine HNC (NH2)2 is a stronger base than methylamine, CH3NH2 I am confused by this because I assumed that the least stable compound would be the most basic Guanidine is resonancestabilized, which means it should be less basic than methylamine

23 1 Properties Of Amines Organic Chemistry Ii
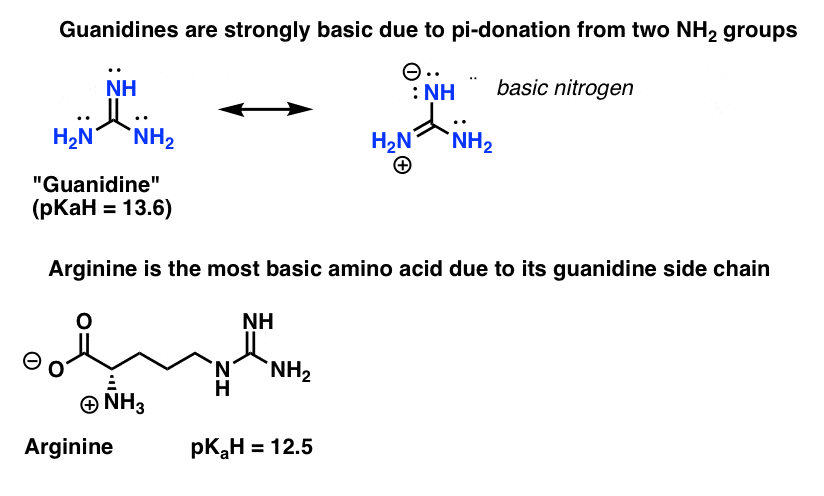
Guanidine group has a basicity stronger than ammonia due to
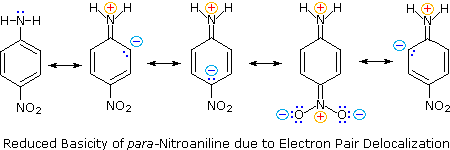
Guanidine group has a basicity stronger than ammonia due to-2322 22 Example BasicityAromatic Amines Example BasicityAromatic Amines 3nitroaniline is a stronger base than 4Nitroaniline NH 2 O 2 N NH 2 O 2 N p K a 10 p K a 247 4Nitroaniline 3Nitroaniline delocalization of the nitrogen lone pair onto the oxygen atoms of the nitro group N NH 2 NH 2 N O O O O Cannot do this kind of ) as a proxy for strong bases that may be present in the atmosphere and explore the molecular interaction between sulfuric acid and guanidine Guanidine is a strong organobase with a pK a value of 136 in water solution, where it is protonated and forms the guanidinium cation (C(NH 2) 3 )28 Guanidine contains one imino group and two amino groups




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Arrange The Following In The Order Of Increasing Basicity P Toluidine N N Dimethyl P Toluidine P Nitroaniline Aniline I I T 1986
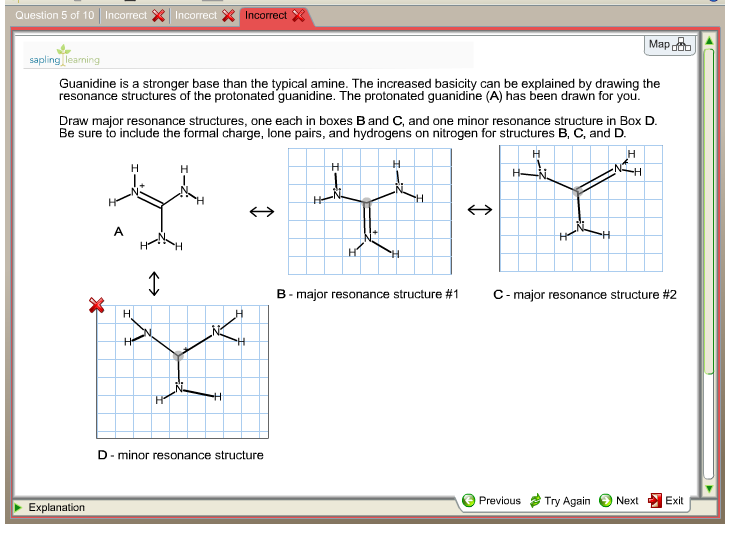
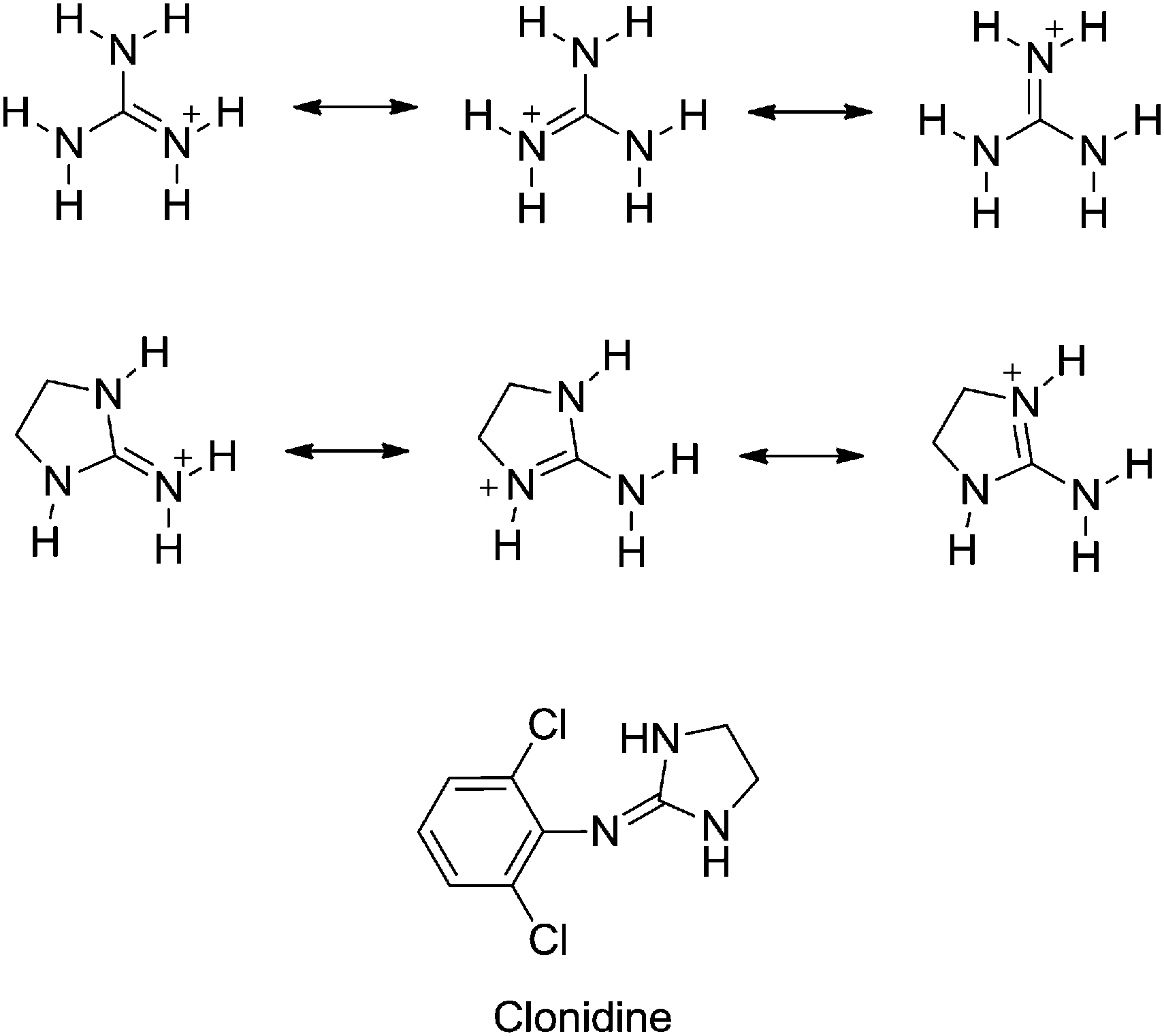
Transcribed image text Guanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you Draw major resonance structures, one each in boxes B and C, and one minor resonance structure in Box D Be sure toAddictive Alkaloids Since ancient times, plants have been used for medicinal purposes One class of substances, called alkaloids, found in many of these plants has been isolated and found to contain cyclic molecules with an amine functional groupThese amines are bases They can react with H 3 O in a dilute acid to form an ammonium salt, and this property is used to extract themHowever, guanidine has a pKa of 125(3) and should exist almost entirely as a cation under environmental conditions (pH 59)(SRC) As a result, guanidine may have greater adsorption and less mobility than its estimated Koc value indicates since cations generally adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than neutral
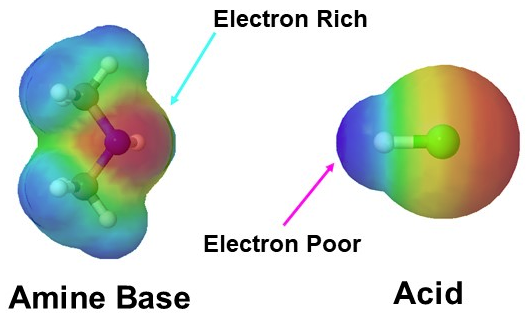
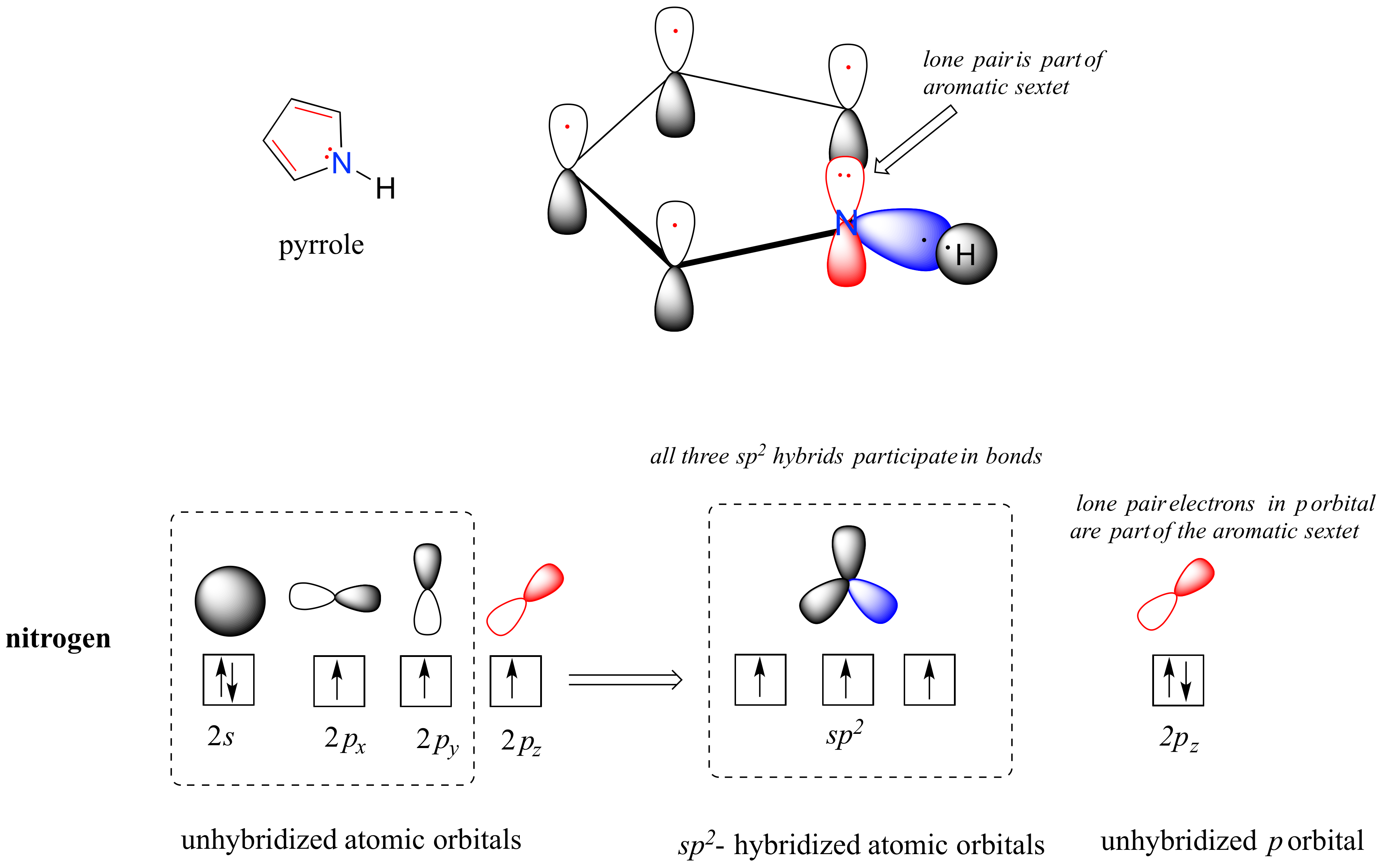
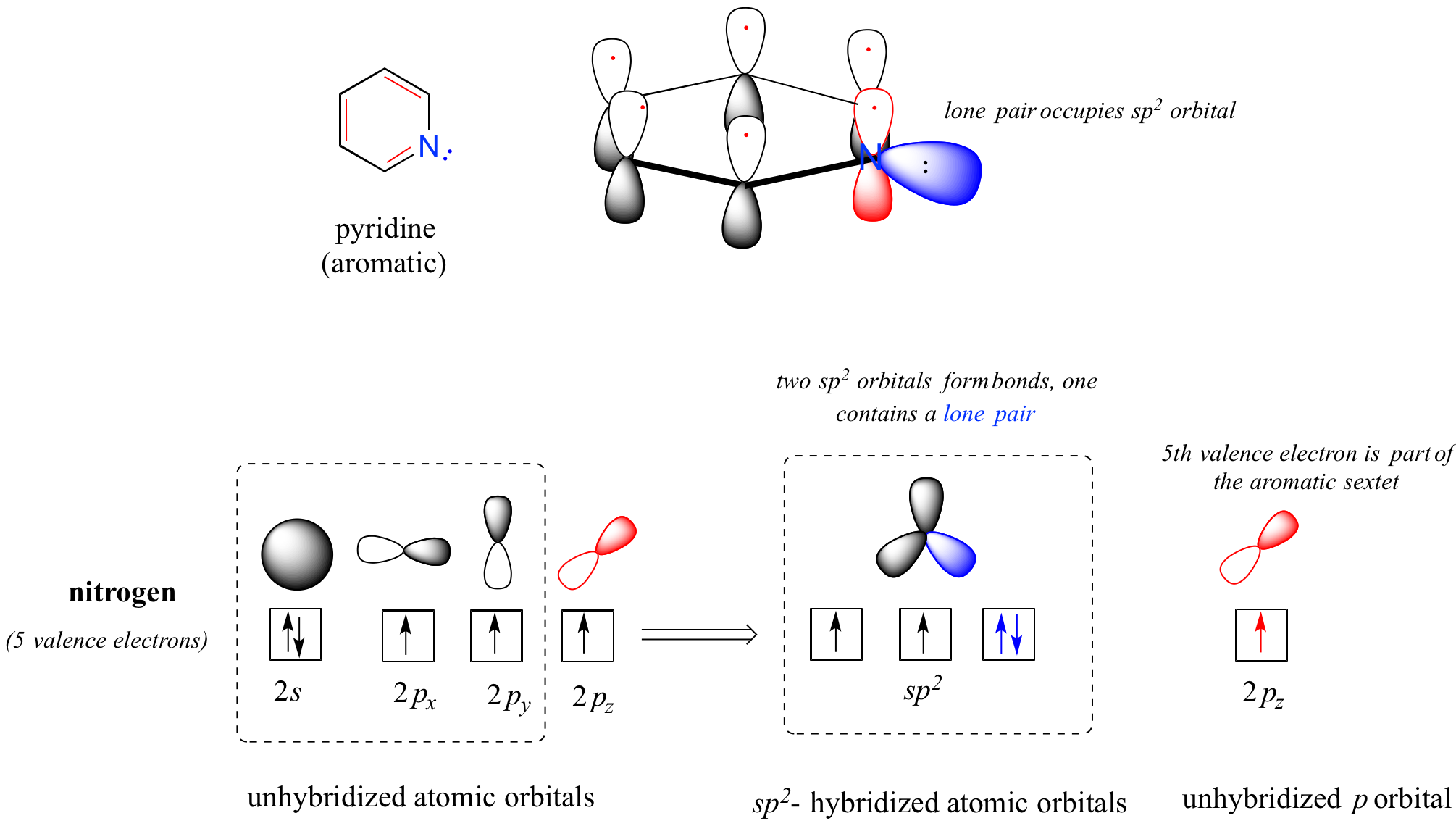
In chemistry, there are three definitions in common use of the word base, known as Arrhenius bases, Brønsted bases, and Lewis basesAll definitions agree that bases are substances which react with acids as originally proposed by GF Rouelle in the mid18th century Svante Arrhenius proposed in 14 that a base is a substance which dissociates in aqueous solution to formStronger base than pyridine positive charge on the imidazolium ion is delocalized on both nitrogen atoms of ringdecreased basicity due to lone pair on sp2 orbital, part of the aromatic sextet, unavailable to protonate ion (pKa=695) METHYLAMINE #"CH"_3"NH"_2# contains a methyl group, which is electrondonating That is, it inductively donates electrons through the #"N""Br"# bond towards nitrogen, which "activates" the nitrogen's Lewis base behavior since there is more electron density around it The more electron density around the nitrogen, the more it has available to donate to something
Among the common amino acids, five have a side chain A guanidine group also appears in larger organic molecules, including on the side chain of arginine (a basic amino acid) It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosives We have to note, however, that the technology of such salts production presents significant difficulties due to low basicity of nitronium cation However, way is known for production of nitronium derivatives in anhydrous environments, such as acetyl nitrite, solution of benzoylnitrite in acetic anhydride, 13 as well as a solution of




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine




Guanidine Catalyzed Asymmetric Strecker Reaction Modes Of Activation And Origin Of Stereoselectivity
Note that the strongest acid is ammonia This means that ammonia is the weakest base of the four bases Basicity order is ammonia primary amine secondary amine tertiary amineGuanidine bases have been used as a basic catalyst and enantiomerically pure guanidine derivatives are expected to promote the asymmetric Henry reaction The first report on the chiral guanidinecatalyzed asymmetric Henry reaction was produced by Najera and coworkers in 1994 80 They prepared chiral guanidine such as 23 or 24 and observed moderate enantioselectivitiesGuanidine is a stronger base than the typical amine The increased basicity can be explained by drawing the resonance structures of the protonated guanidine The protonated guanidine (A) has been drawn for you Draw major resonance structures, one each in boxes B and C, and one minor resonance structure in Box D Be sure to include the formal charge,



Amine Chemistry Tutorial



2
A basic tertiary amino group with a pKa of 86 (conjugate acid approx 90% ionised at physiological pH) and so its predominantly protonated and positively charged at physiological pH vital for ability to interact with the at mopioid receptor which has a– Hydrogen bonds from N—H's are not as strong as those resulting from O—H's – Hydrogen bonding between 1° and 2° amines is not as strong as those found in alcohols or carboxylic acids • 1° and 2° amines have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular weight • 3° amines, since they do not hydrogen bond to eachNatural guanidines are a class of secondary metabolites characterized by the presence of the guanidine functionality, which is of limited occurrence in nature in natural products other than peptides produced by nonribosomal peptide synthetases or ribosomes, 1–10 since many peptides contain arginine in their structures Natural guanidines are commonly produced by bacteria and



Amine Reactivity




Amines 23 1 Structure Classification U Amines Are
We recall that a guanidine structure is known from the cocrys wwwchemeurjorg tals of C 5 H 8 N 4 CH 5 N 3 and C 5 H 8 N 4 (CH 5 N 3 ) 2 based on singlecrystal Xray diffraction data atThe nitrogen is more negative in methylamine than in ammonia, and so it picks up a hydrogen ion more readily The ion formed from methylamine is more stable than the one formed from ammonia, and so is less likely to shed the hydrogen ion again Taken together, these mean that methylamine is a stronger base than ammoniaGuanidine, an organic compound of formula HN=C(NH 2) 2It was first prepared by Adolph Strecker in 1861 from guanine, which had been obtained from guano, and this is the origin of the nameThe compound has been detected in small amounts in a variety of plant and animal products, but some of its derivatives are widely distributed and are of considerable importance, especially in the



Welcome To Chem Zipper Com December 19



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com
In triphenyl amine (3), the lone pair of nitrogen is in conjugation with phenyl groups and thus would be least available for protonation Due to resonance structures of guanidine (2), it should be the strongest base While in case pyridine already has a stable conjugated system of three double bonds in an aromatic ring, like benzene Hence the lone pair electrons on the N atom in pyridine is localized and more available for donation and easily donated to a H ions Therefore, pyridine is a stronger base than PyrroleAnother example is guanidine which is a very strong base in aqueous solution (pK a > 13), whereas in the gas phase its basicity is lower than that of triethylamine 3, 58 Hence, it is possible



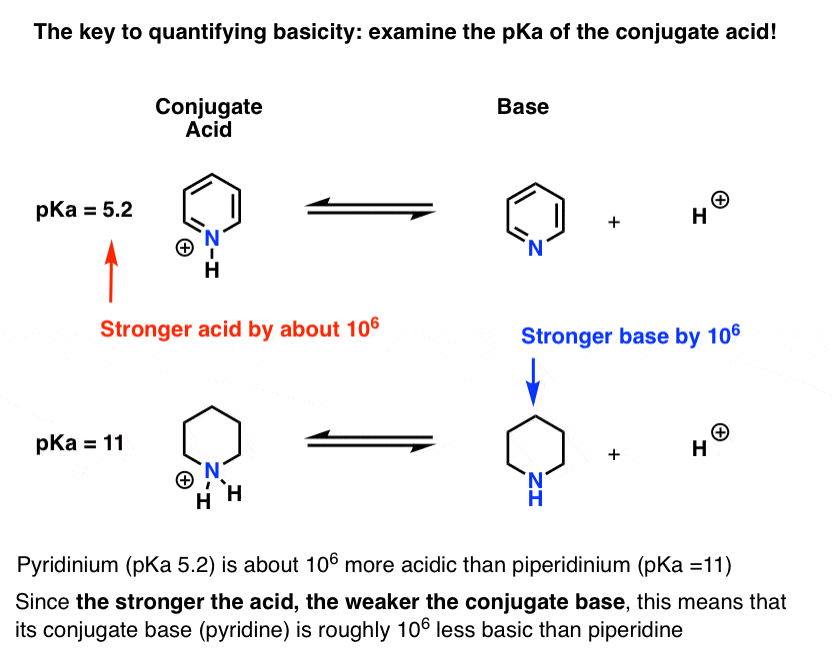
Amine Basicity Is Measued By The Pka Of Its Conjugate Acid Pkah



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues
Guanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH 2) 2It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosivesIt is found in urine as a normal product of protein metabolismA guanidine moiety also appears in larger organic molecules, including on the side chain of arginineImidazole is over a million times more basic than pyrrole because the sp 2 nitrogen that is part of one double bond is structurally similar to pyridine, and has a comparable basicity Although resonance delocalization generally reduces the basicity of amines, a dramatic example of the reverse effect is found in the compound guanidine (pK a = 13The greatly reduced basicity of canavanine is due of course to the oxygen atom in the hydroxyguanidine struc tural unit In fact, this guanidinooxy group in canavanine is a weaker base than ammonia This reduced basicity makes it easier to obtain canavanine in the f r ee crystal




Pdf Guanidine A Highly Efficient Stabilizer In Atmospheric New Particle Formation



Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine
Aliphatic amines (pKb = 3 to 422) are stronger bases than ammonia (pKb =475) due to I effect of alkyl groups which increases e density at nitrogen atom In gaseous phase R3N > R2NH > RNH2 > NH3 (governed by I effect of Alkyl groups) Arylalkyl amines have amine groups indirectly attached to aromatic ringsAnswer (1 of 2) There is a nitrogen group that can accept a proton, just like in ammonia Imidazole is a stronger base than ammonia or a typical amine, because it has resonance stabilization in the protonated form "Amphoteric" means acting as either acid or base, depending on circumstancesBasicity You will recall that the nitrogen atom of ammonia is sp 3 hybridized and there is an unshared pair of electrons in the fourth tetrahedral orbital This makes ammonia a base and a nucleophile Because nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen, ammonia is a much stronger base than water and also a much better nucleophile Amines




A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated B Why Guanidine Is The Strongest Organic N Base K B 1 C Why




A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated B Why Guanidine Is The Strongest Organic N Base K B 1 C Why
In contrast, due to the high basicity of arginine (pK A >12) 21 and the propensity for esters to hydrolyze under highly basic aqueous conditions, condensed phase reactions with arginine are restricted to very specific reaction conditions in anhydrous solvents with reaction times requiring several days 22 For this reason, there has been littleGuanidine is the compound with the formula HNC(NH 2) 2It is a colourless solid that dissolves in polar solvents It is a strong base that is used in the production of plastics and explosivesIt is found in urine as a normal product of protein metabolismA guanidine moiety also appears in larger organic molecules, including on the side chain of arginineBasicityGuanidine u Guanidine is the strongest base among neutral organic compounds • Its basicity is due to the delocalization of the positive charge over the three nitrogen atoms 23 25 Reaction with Acids u All amines, whether soluble or insoluble in water, react quantitatively with strong acids to form watersoluble salts 23 26




A Which N Of Guanidine I Is More Basic And Is More Likely To Be Protonated B Why Guanidine Is The Strongest Organic N Base K B 1 C Why



Exam 3 Answer Key
Q Guanidine group has a basicity stronger than ammonia due to alpha effect a O none of them b O elec A Guanidine bases have stronger basicity than ammonia as in guanidine, alkyl groups donate electron deImidazole is more than a million times more basic than pyrotechtle because the nitrogen sp2 that is part of a double link is structurally similar to pyridine, and has a comparable basicity Although resonance offshoring generally reduces the basicity of amines, a dramatic example of the reverse effect is found in compound guanidine (pKa = 136)The guanidine is among the stronger bases known (organic nitrogenous) with a pK a of 136 (but less stronger than tetraalkyl ammonium hydroxides) Both the neutral molecule and the cation, H 2 N ⊕ = C(NH 2 ) 2 , resulting from its protonation are stabilized by delocalisation



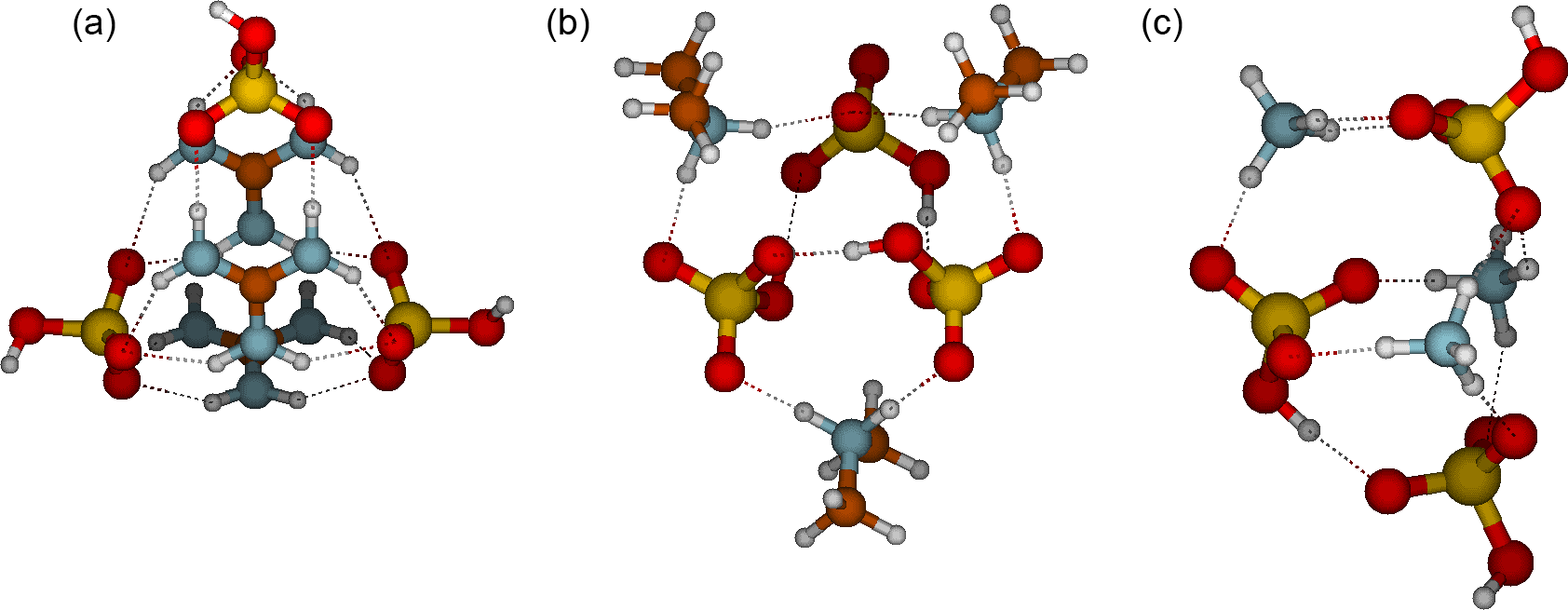
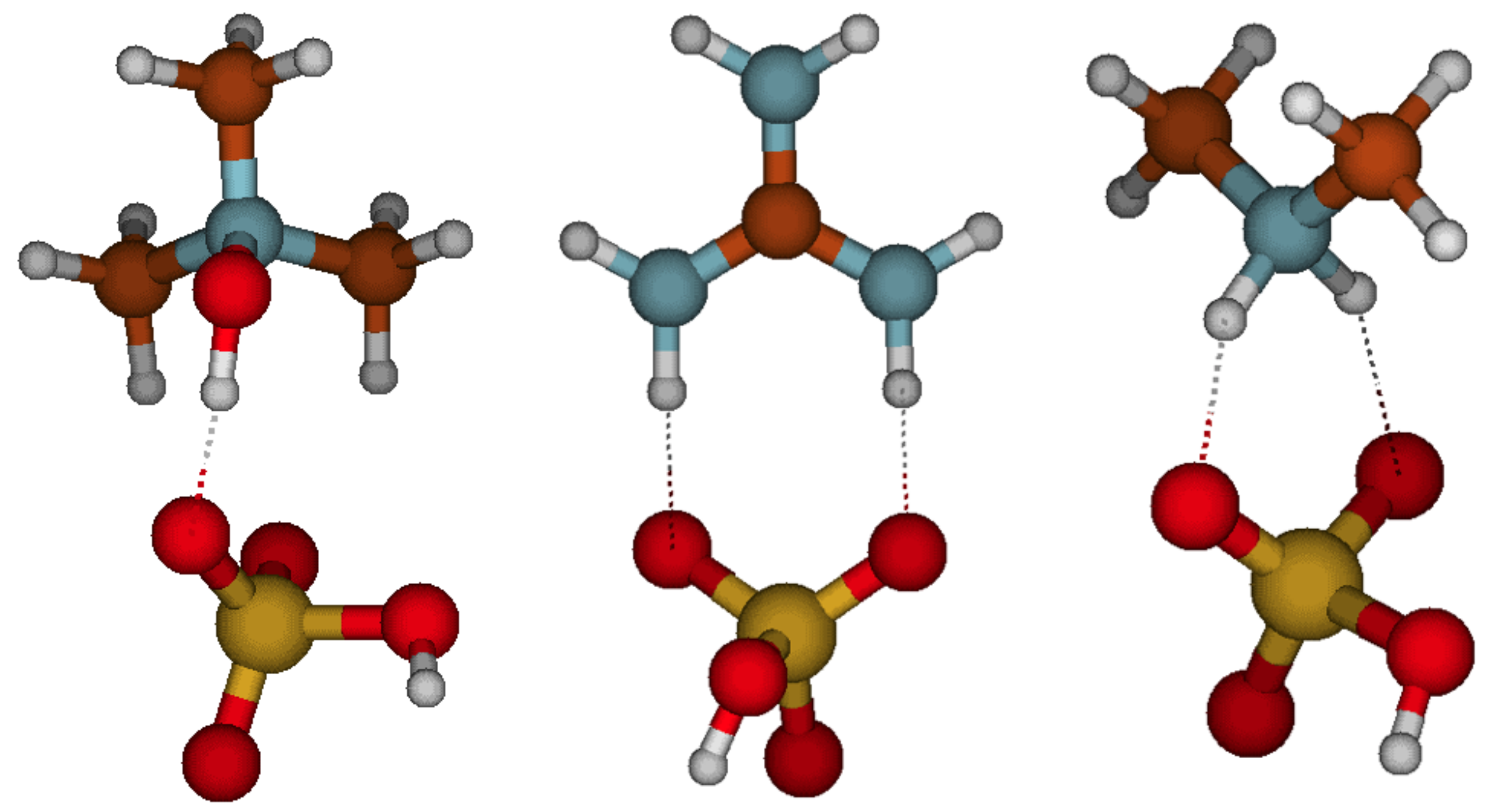
Acp Role Of Base Strength Cluster Structure And Charge In Sulfuric Acid Driven Particle Formation




Basic Principles Of Organic Chemistry Pages 51 99 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
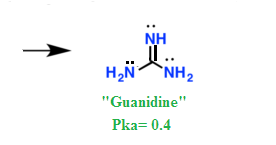
In this case with guanidine there are two protonation equilibria occurring in parallel Even though protonation of the s p X 3 nitrogen is kinetically favored due to its increased basicity, the product we observe is from protonation of the s p X 2 nitrogen due to its greater thermodynamic stability Because both of these processes are in Imidazole is over a million times more basic than pyrrole because the sp 2 nitrogen that is part of one double bond is structurally similar to pyridine, and has a comparable basicity Although resonance delocalization generally reduces the basicity of amines, a dramatic example of the reverse effect is found in the compound guanidine (pK a = 136) With a pK b of 04, guanidine is a strong base Most guanidine derivatives are in fact salts containing the conjugate acid ) This planar, symmetric ion consists of three amino groups each bonded to the central carbon atom with a covalent bond of order 4/3 What amino acids have a charge?




Which Nitrogen Is Protonated Readily In The Guanidine Ltimg Youtube



16 4 Basicity Of Amines Chemistry Libretexts
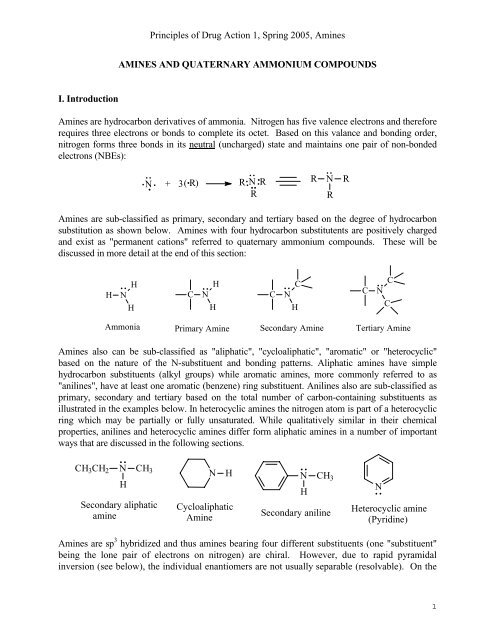
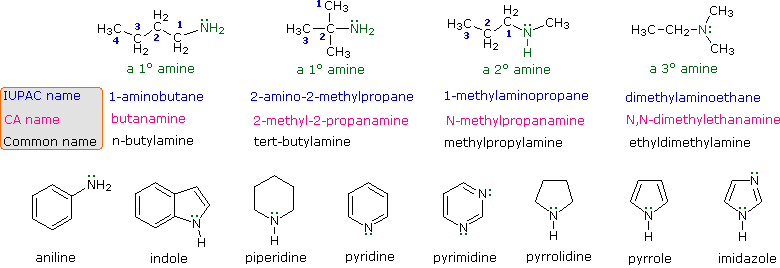
An amine is an organic compound, related to ammonia, that contains a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more alkyl groups on each molecule "Primary amine" "an example of Secondary amine" "Tertiary amine" Nitrogen atoms that are part of an aromatic ring have planar configuration(sp2 configuration ) and not stereogenic centresBecause of aromacity amines inSolution for Guanidine group has a basicity stronger than ammonia due to alpha effect a O none of them b O electronegativity effect of nitrogen c O Inductive Answered Guanidine group has a basicity stronger bartleby



Amine Reactivity




Amines 23 1 Structure Classification U Amines Are



Why Is Guanidine Such A Strong Base Quora



Topic 2




Why Is Guanidine Such A Strong Base Quora




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Give An Explanation For The Fact That Guanidine Nh C Ch3 2 Is A Stronger Base Than Most Of Amines




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Give An Explanation For The Fact That Guanidine Nh C Ch3 2 Is A Stronger Base Than Most Of Amines




Ao4c4 Wlllj6m



Acp A Predictive Model For Salt Nanoparticle Formation Using Heterodimer Stability Calculations




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Arrange In Correct Order Of Basic Character Of Aniline Pyrrol Pyridine And Piperidine




Pdf Role Of Base Strength Cluster Structure And Charge In Sulfuric Acid Driven Particle Formation




Amines Bloomsburg Area School District Overview 10 1 How To Predict The Relative Basicity Of Pdf Document




Solved Explain This Resonance And Basicity Problem Why Does Chegg Com



22 2 Basicity Of Amines And Ammonium Salt Formation Chemistry Libretexts



Acp Role Of Base Strength Cluster Structure And Charge In Sulfuric Acid Driven Particle Formation



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry




Why Are Amidines More Basic Than Amines Chemistry Stack Exchange




23 1 Properties Of Amines Organic Chemistry Ii




10 1 Chemistry 60 Spring 60 Lsu Chapter 10 Amines Sections Ppt Download




Organic Chemistry William H Brown Christopher S Foote Ppt Video Online Download




23 1 Properties Of Amines Organic Chemistry Ii




5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry




Anhydrous Proton Conducting Material Consisting Of Basic Protein Protamine Sciencedirect




Guanidines From Toxic Substances To Compounds With Multiple Biological Applications Detailed Outlook On Synthetic Procedures Employed For The Synthesis Of Guanidines Sciencedirect
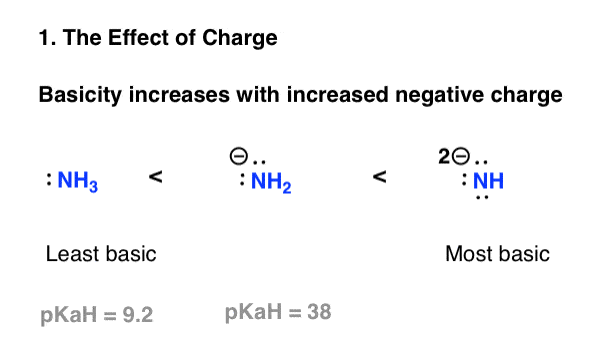



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry



Solved Guanidine Pka 13 6 Is A Very Strong Base Almost As Basic As Hydroxide Ion A Complete




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com N N 2 6 Tetramethyl Aniline Is More Basic Than N N Dimethyl Aniline Why



Atmosphere Free Full Text Enhancing Potential Of Trimethylamine Oxide On Atmospheric Particle Formation Html
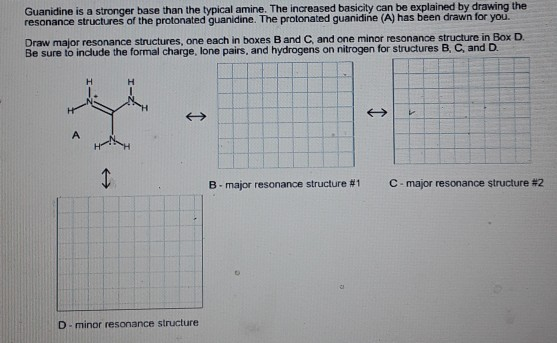



Solved Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine Chegg Com



Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues




Why There Is A Huge Difference Between The Basicity Of Urea And Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry



Amine Reactivity



Solved B 4 Points Briefly Explain Why Guanidine Is A Much Stronger Base Than Most Other Amines Course Hero




One Pot Synthesis And Application Of Novel Amino Functionalized Silica Nanoparticles Using Guanidine As Amino Group New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing




23 1 Properties Of Amines Organic Chemistry Ii




Amines The Organic Bases Categorizing Amines N Amines
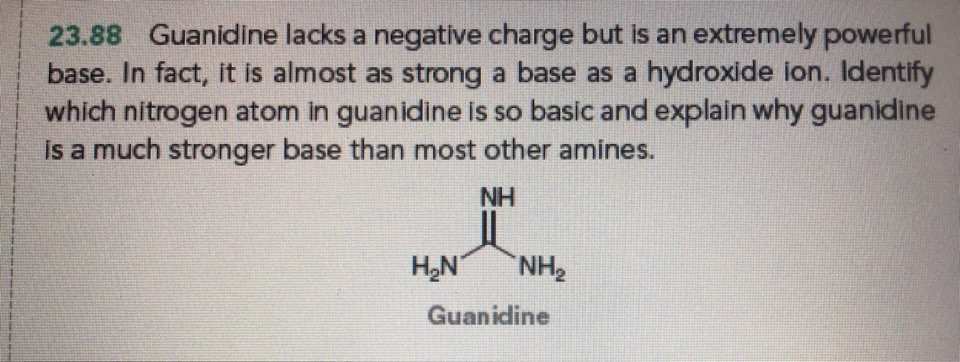



Solved 23 Guanidine Lacks A Negative Charge But Is An Chegg Com




Guanidine Nh 2 2 C Nh Is Said To Be The Strongest Nitrogen Containing Organic Base Because




Why Guanidine Is Worlds Strongest Base Iit Jee Vineet Khatri Atp Star Youtube



Substituent Effects On The Basicity P K A Of Aryl Guanidines And 2 Arylimino Imidazolidines Correlations Of Ph Metric And Uv Metric Values With P New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C7nje




Guanidine Formula Uses Facts Britannica




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Amines Are More Basic Than Ammonia Why



Why Is Guanidine Such A Strong Base Quora



22 2 Basicity Of Amines And Ammonium Salt Formation Chemistry Libretexts



Amine Basicity Is Measued By The Pka Of Its Conjugate Acid Pkah




Amines Bloomsburg Area School District Overview 10 1 How To Predict The Relative Basicity Of Pdf Document




Protonation Of Guanidine Chemistry Stack Exchange




Amines 23 1 Structure Classification U Amines Are




Cimetidine A Rational Approach To Drug Design By



1




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine



1
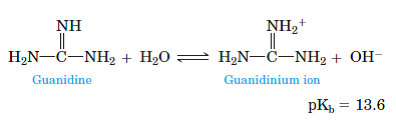



Solved Guanidine Pka 13 6 Is A Very Strong Base Almost As Basi Chegg Com




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Arrange The Following In The Order Of Increasing Basicity P Toluidine N N Dimethyl P Toluidine P Nitroaniline Aniline I I T 1986




Amine Reactivity




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com What Is Relative Basic Strength Order 1 Amines 2 Amines And 3 Amines Explain




5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry




Organic Chemistry Flashcards Quizlet




Guanidine And Guanidinium Cation In The Excited State Theoretical Investigation The Journal Of Chemical Physics Vol 141 No 7




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine



2
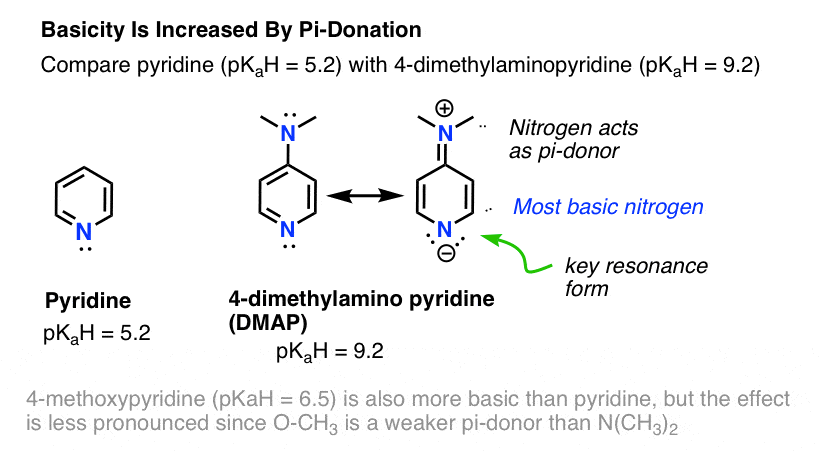



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry




Guanidines From Toxic Substances To Compounds With Multiple Biological Applications Detailed Outlook On Synthetic Procedures Employed For The Synthesis Of Guanidines Sciencedirect




Pdf Guanidine A Simple Molecule With Great Potential From Catalysts To Biocides And Molecular Glues



160
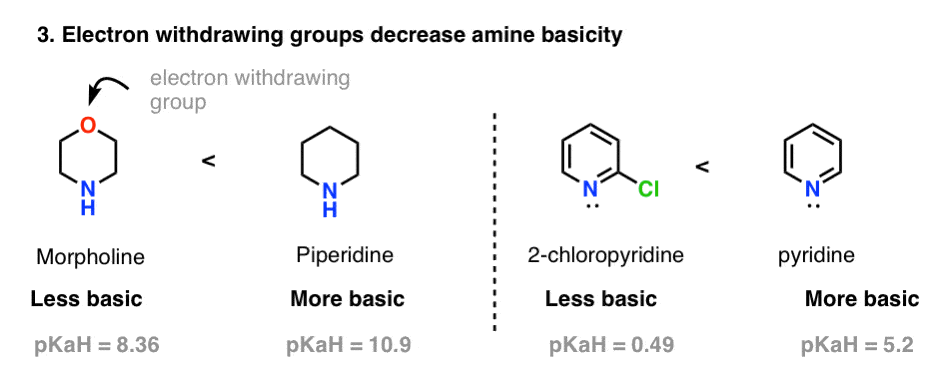



5 Key Basicity Trends Of Amines Master Organic Chemistry



16 4 Basicity Of Amines Chemistry Libretexts




Amines The Organic Bases Categorizing Amines N Amines




Acp Role Of Base Strength Cluster Structure And Charge In Sulfuric Acid Driven Particle Formation




Single Crystal Structure Hydrogen Bonding Interaction Charge Transfer And Thermal Properties Of A New Guanidine Derivative Crystal Phosphate Bis Guanidinoacetate Sciencedirect




Development Of A Rapid Gc Fid Method To Simultaneously Determine Triethylamine Diisopropylamine And 1 1 3 3 Tetramethylguanidine Residues In An Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Sciencedirect




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Arrange The Following In The Order Of Increasing Basicity P Toluidine N N Dimethyl P Toluidine P Nitroaniline Aniline I I T 1986



1




Pdf Guanidine A Highly Efficient Stabilizer In Atmospheric New Particle Formation




Gas Phase Proton Affinities Pas And Basicities Gbs In Kcal Mol A1 Download Scientific Diagram



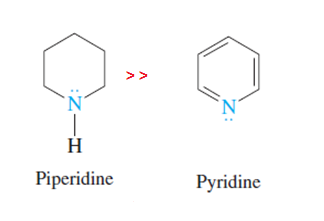
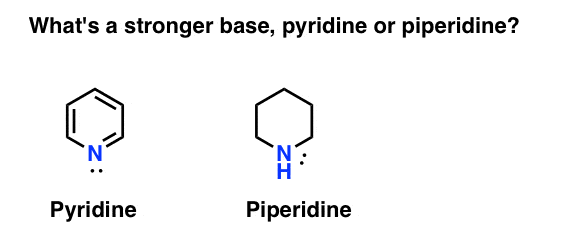
Is Piperidine More Basic Than Pyridine Quora




Pdf Role Of Base Strength Cluster Structure And Charge In Sulfuric Acid Driven Particle Formation
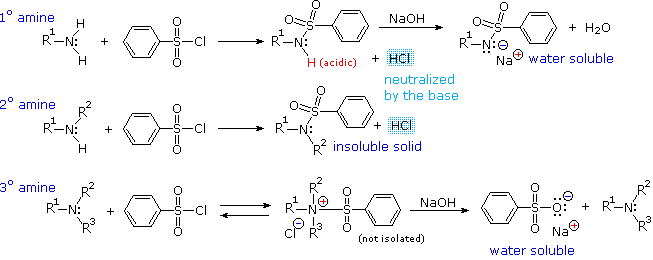



Amine Reactivity



Chemical Forums Resonance And Basicity




Canonical Deprotonated Or Zwitterionic Ii A Computational Study On Amino Acid Interaction With The Tio2 110 Rutile Surface Comparison With The Anatase 101 Surface Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing




Pdf Guanidine A Highly Efficient Stabilizer In Atmospheric New Particle Formation




Welcome To Chem Zipper Com Basicity Of Guanidine




Guanidine Is A Stronger Base Than The Typical Amine The Increased Basicity Can Be Explained By Brainly Com


